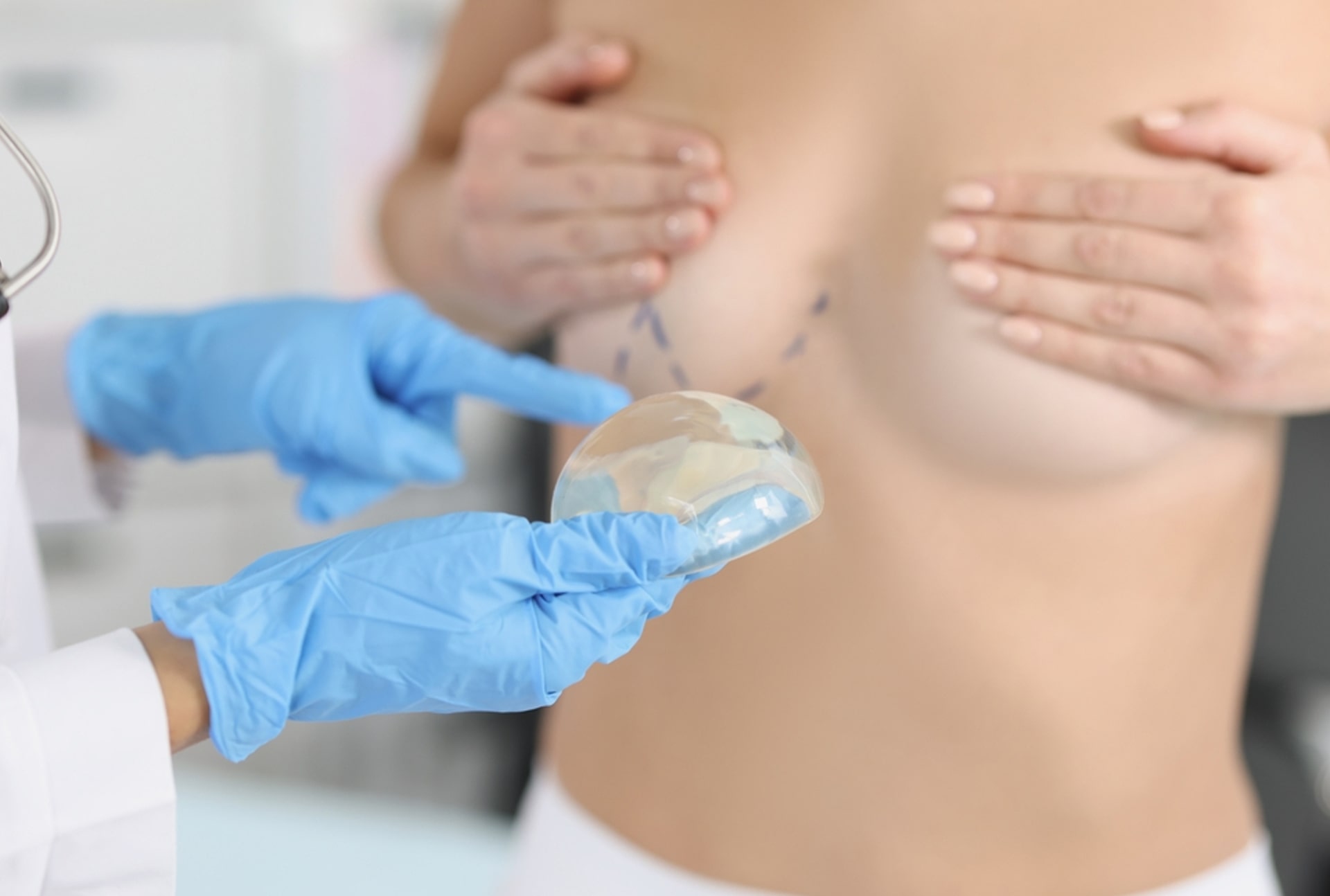
Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure aimed at making women’s breasts fuller, more symmetrical, and aesthetically pleasing. This procedure is commonly chosen by women who are dissatisfied with the size of their breasts for various reasons. Breast augmentation can be performed for aesthetic purposes, to correct post-pregnancy changes, or to meet the needs of women with smaller breasts due to genetic factors.
Reasons for Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation is typically preferred for the following reasons:
- Aesthetic Goals: Ideal for women who desire fuller and more proportionate breasts.
- Post-Pregnancy Changes: Can compensate for volume loss in the breasts due to pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Symmetry Correction: Also used to correct asymmetrical breast appearance.
Surgical Process
Breast augmentation is generally carried out in the following steps:
- Consultation and Planning:
- During the initial consultation, the patient’s expectations, health condition, and ideal breast size are determined.
- The surgeon provides information about the type of implant (saline or silicone) and placement method.
- Surgical Procedure:
- The surgery, performed under anesthesia, usually takes 1-2 hours.
- Three main methods can be used for implant placement:
- Subglandular Placement: The implant is placed over the breast tissue, under the glandular tissue.
- Subpectoral Placement: The implant is placed under the pectoral muscle; this method offers a more natural look.
- Incision Sites: The implant can be placed through various incisions (transareolar, inframammary, or axillary), each offering different advantages.
- Recovery Process:
- Patients are typically discharged the same day, but a few days of rest are recommended.
- The recovery period usually lasts 4-6 weeks, with swelling and bruising being normal during this time.
- Sutures are usually removed within 1-2 weeks.