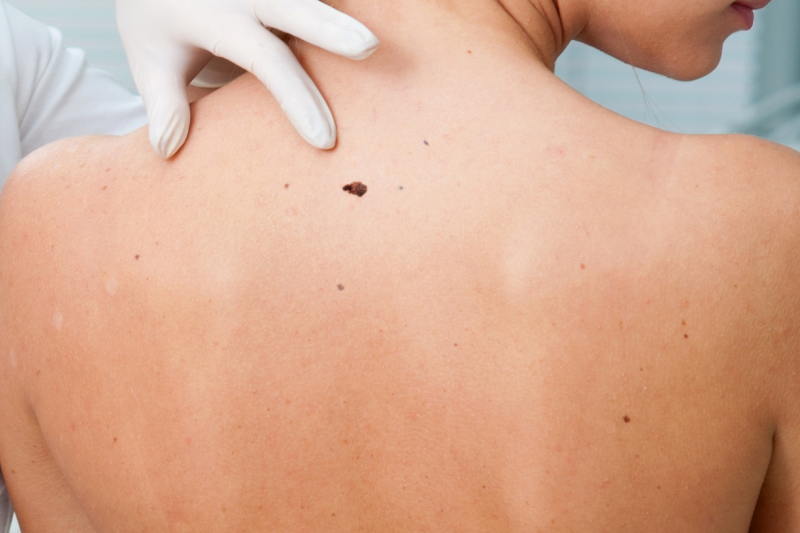
Skin cancers develop from the uncontrolled growth of skin cells and are classified into the most common types: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Risk factors such as prolonged exposure to harmful UV rays from the sun, the use of tanning beds, genetic factors, and having fair skin increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Early diagnosis leads to higher treatment success rates, making regular skin examinations and monitoring suspicious lesions extremely important. The treatment of skin cancers is planned according to the type, stage, and overall health condition of the patient.
Skin Cancer Treatment Methods
- Surgical Intervention: Surgical removal of cancerous tissue is one of the most common treatment methods for skin cancer. In basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, part of the healthy tissue surrounding the tumor is also removed to reduce the risk of recurrence. Mohs surgery, a technique often used for facial cancers, minimizes the removal of healthy tissue while ensuring aesthetic results by removing only the cancerous tissue.
- Cryotherapy (Freezing): For early-stage skin cancers, cancerous cells are destroyed by freezing them with liquid nitrogen. This method is particularly effective for superficial basal cell carcinomas.
- Laser Treatment: Laser light is used to destroy cancerous cells. This method is preferred for superficial lesions, particularly for small skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma.
- Radiotherapy: For cancers that are not suitable for surgery or are in advanced stages, radiotherapy is used to destroy tumor cells. It is typically applied to eliminate cancer cells left after surgery or as the primary treatment for very large tumors.
- Topical Chemotherapy: For early-stage skin cancers, chemotherapeutic creams directly applied to the skin target cancer cells. This method is often used in cases where surgery is not necessary, especially for superficial cancers.
- Immunotherapy: In advanced melanoma cases, immunotherapy activates the immune system to fight cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs are particularly effective in treating metastatic melanoma.
- Targeted Therapy: In certain melanoma types caused by genetic mutations, targeted drugs are used to stop tumor cell growth signals. This treatment aims to destroy cancer cells and prevent them from spreading to other areas.
Post-Treatment and Preventive Measures
After treatment, regular dermatologist check-ups help minimize the risk of cancer recurrence. Using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding sun exposure, especially during peak sunlight hours, are highly effective in reducing the risk of skin cancer. For individuals at higher risk, regular skin examinations are essential for early diagnosis and successful treatment.